一. 免疫治疗与介入治疗的关系:联合关系 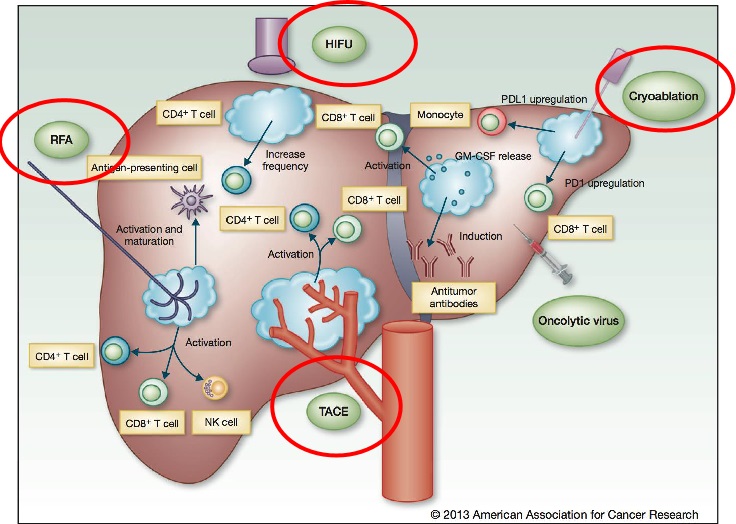 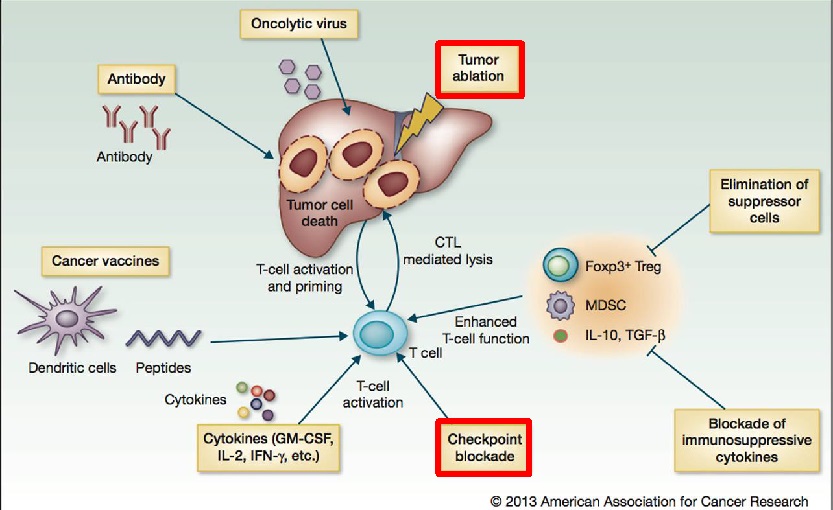
Checkpoint Inhibitors + IO
检查点抑制剂+肿瘤介入
https://www.smartpatients.com/pathways/pd-1
检查点抑制剂
The immune system plays an important role in controlling anderadicating cancer.
免疫系统在控制癌症中起着重要的作用。
Nevertheless, in the setting of malignancy, multiple mechanisms of immune suppression may exist that prevent effective antitumor immunity.
然而,在恶性肿瘤的情况下,可能存在多种免疫抑制机制来阻止有效的抗肿瘤免疫。
Antibody therapy directed against several negative immunologic regulators (checkpoints) is demonstrating significant success and is likely to be a major component of treatment for patients with a variety of malignancies
针对几个阴性免疫调节剂(检查点)的抗体治疗显示出显著的成功,并可能成为治疗各种恶性肿瘤患者的重要组成部分。
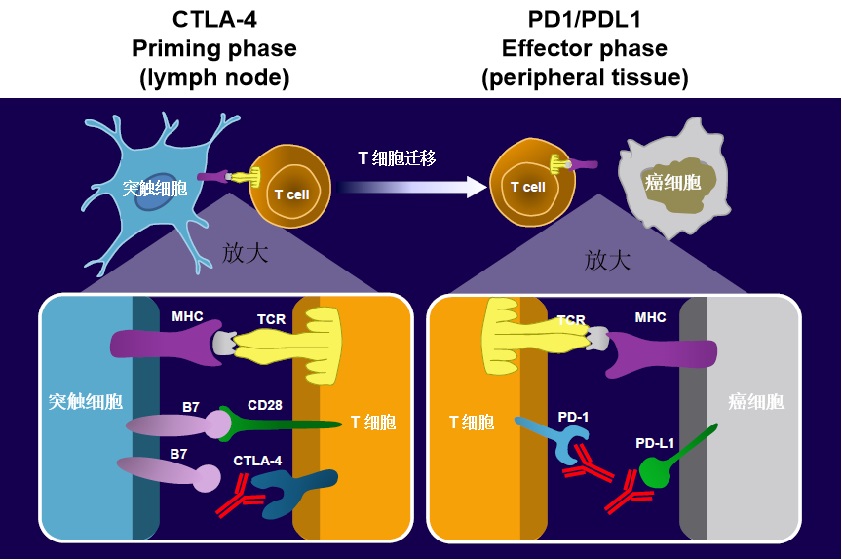
CTLA4 和 PD1或 PDL1分别作用于癌免疫循环不同阶段,和不同的细胞。
肝癌:消融或D-TACE+免疫治疗
Checkpoint Inhibitor: Anti-CTLA4
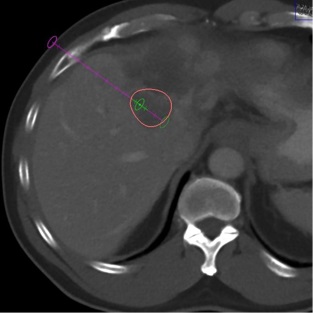
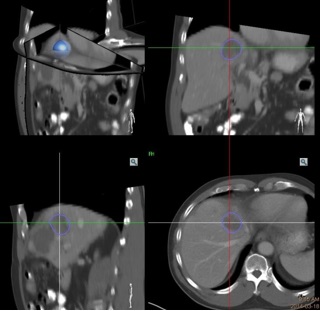
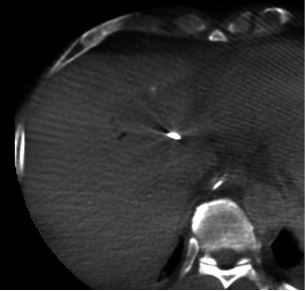
CBCT Fusion To Target Viable Part of Tumor
RFA (or TACE) + Anti-CTLA4 Checkpoint Inhibitor for Hepatoma
Tremelimumab Plus Ablation / TACE
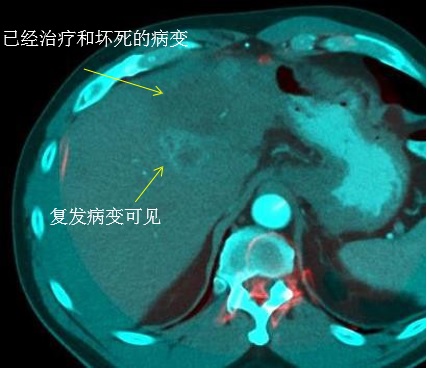
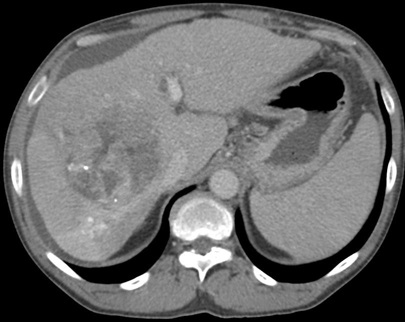
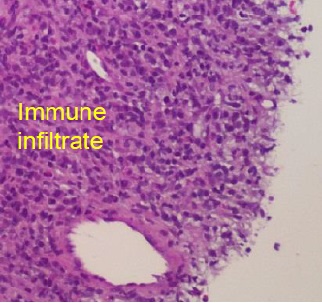
Can see pseudoprogression on CT / MRI as a result of an immunologic infiltrate
12/14 HCV Reduced viral load
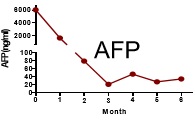
Reduced AFP
6 week biopsy: CD8 up only if response
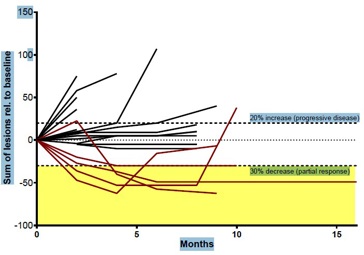
57% PFS @ 6 mo – heavily pre-treated pts
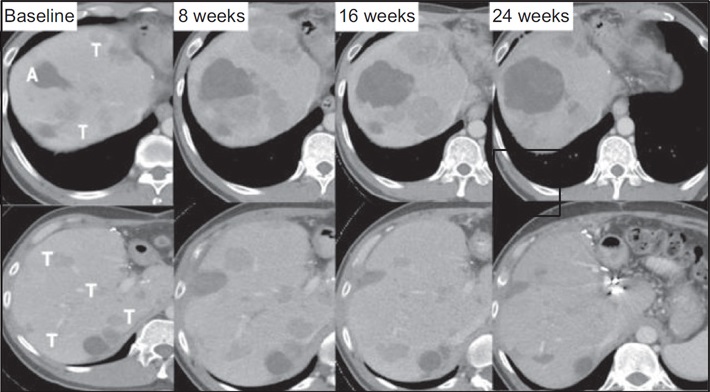
CT扫描在6个月的时间内显示肿瘤面积(表示T)从基线的10.5厘米明显减少到2个月后的4.3厘米。 值得注意的是,虽然这个病人确实经历了TACE次栓塞,但图中所示的其它肿瘤肿块并没有栓塞。 起初有扩大趋势,但随着时间的推移,没有栓塞的病灶也逐渐消失。
RFA (or TACE) + Anti-CTLA4 Checkpoint Inhibitor for Hepatoma
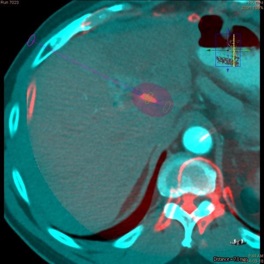
Remote tumor Post Anti-CTLA4 & Ablation
抗CTLA4和消融后远处肿瘤(非治疗的肿瘤)的改变
Can see pseudoprogression on CT / MRI as a result of an immunologic infiltrate
Greten & Duffy ASCO 2015, ASCO GI 2016, J Heptology 2016
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|