| Gold Standard: Surgical Resection
Standard of care for early stage NSCLC (80 % of primary lung cancers)
Surgery depends on:
Abbas G, et al.Radiofrequency and microwave ablation of lung tumors. J Surg Oncol 2009; 100:645-50.
Gold Standard: Surgical Resection
Churchill ED et al. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surgery 1950;20:349-65.
Ginsberg RJ, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 1995;60(3):613-22. Warren WH. J Thorarc Cardiovsc Surg 1994;107(4):1087-1093. Landreneau RJ. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1997; 113(4):691-8. Abbas G, et al. J Surg Oncol 2009; 100:645-50.
Stage I and II
Surgical Indications for NSCLC: Stages I and II 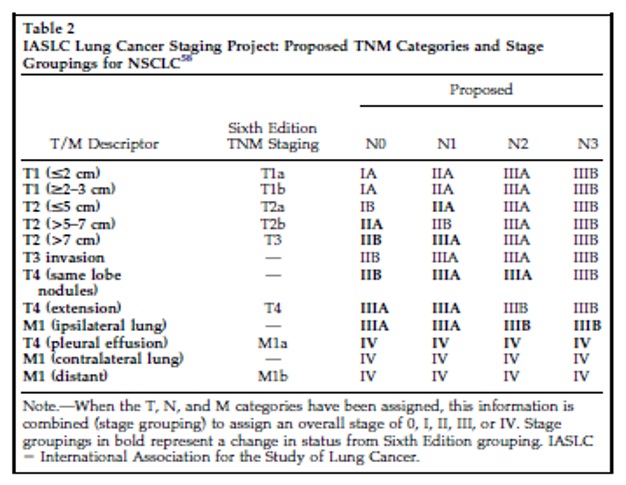 Golstraw P, et al. J Thorac Oncol 2007;2:706-14. Crinò L, et al. Annals of Oncology 2010; 21(S5):103-15. 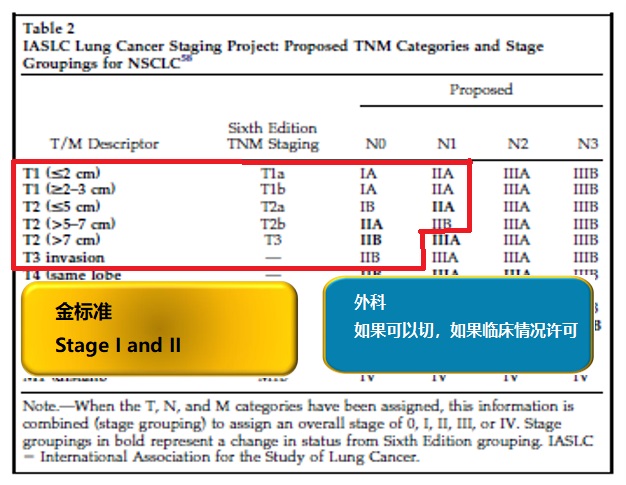
> 15% of patients: tumors deemed surgically unresectable(尽管肿瘤分期低,但位置不适合手术?)
> 30% of patients: >75 years of age or medical inoperability(医学原因不能手术-非解剖因素?)
Goldstraw P, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours.J Thorac Oncol 2007;2:706-14.
Casal RF, et al. Clin Chest Med 2010;31:150-63.
Wolf FJ, et al. Medicine&Health 2009;92(12):407-11.
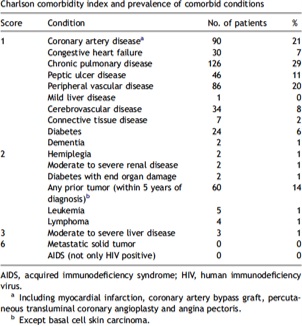
Most frequent comorbidities reported in Literature responsable of Inoperability
- Poor lung function
- Advanced age
- Comorbilities including:
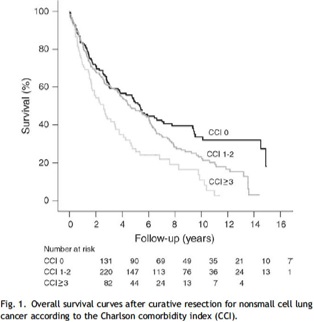
Impact of comorbidities on surgery
Birim Ö et al., Charlson comorbidity index as a predictor of long-term outcome after surgery for nonsmall cell lung cancer 2005, Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg

5-year overall survival: 60-80 % for stage I and 40- 50 % for stage II NSCLC
Surgical Indications for Primary Lung Tumors
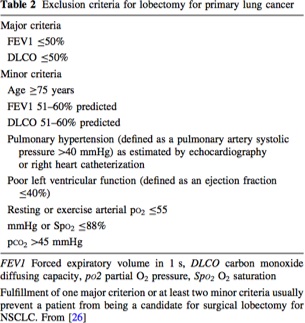
Preoperative evaluation of lung resection candidate

Poonyagariyagorn H, et al. Lung cancer: preoperative pulmonary evaluation of the lung resection candidate.Semin Resp Crit Care Med 2008; 29(3):271-84.
Surgical Indications for Pulmonary Metastases
In the vast majority of cases not indicated for SCLC (since tumor spread at the time of diagnosis)
Patients with significant comorbidities (COPD, ...), are poor surgical candidates (cave: perioperative morbidity and mortality)
Scott WJ et al., Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Stage I and Stage II: ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (2nd Edition) 2007, Chest Pereira PL et al.,Standards of Practice: Guidelines for Thermal Ablation of Primary and Secondary Lung Tumors 2012, Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol (free) Conventional Treatment for NSCLC Stage III 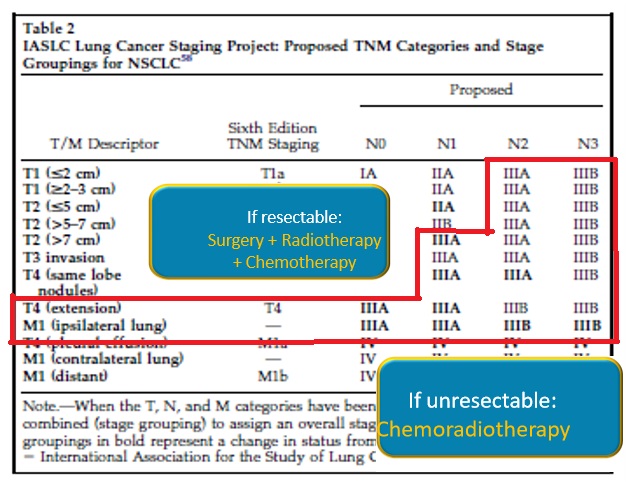
Golstraw P, et al. J Thorac Oncol 2007;2:706-14.
Crinò L, et al. Annals of Oncology 2010; 21(S5):103-15.
Conventional Treatment for NSCLC
Stage IV (palliation):
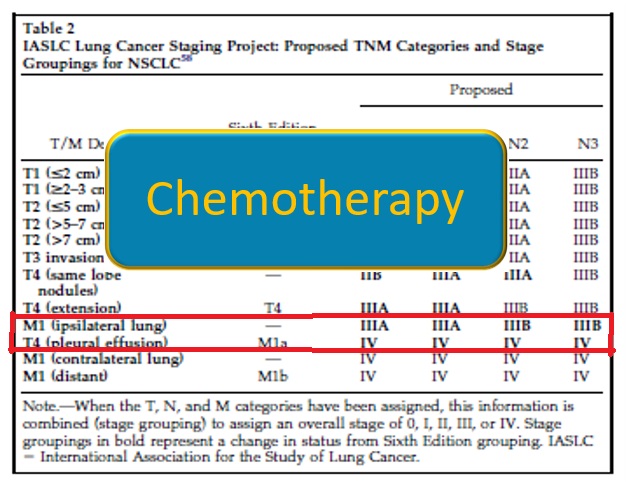
And what to do when surgery is not possible?
  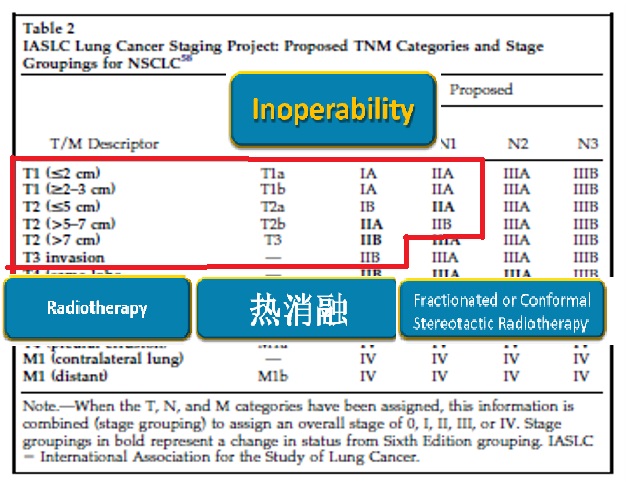
Goldstraw P, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Seventh) Edition of the TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours J Thorac Oncol 2007;2:706-14.
|

|