Percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage
is used to treat a variety of benign and malignant biliary disease
The technique is safe and effective
However, in relatively low incidence, vascular and extra-vascular complications are associated with this technique
In malignant patients, who are frequently severely debilitated by their disease, there is a higher incidence of complications related to percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage 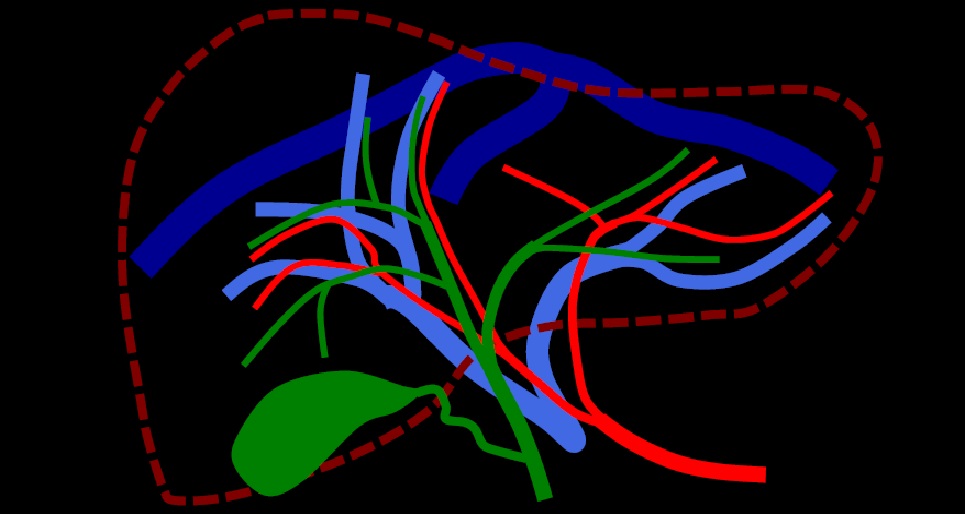
Biliary drainage complications
Transient Fever
Peri-Procedural Venous Biliary Hemorrhage Retraction of Biliary Drainage Bilio-Pleural Fistula Biliary Leakage Biliary Drainage Infection Arterial Biliary Hemorrhage Transient fever: use of antipyretic drugs Peri-procedural Venous Biliary Hemorrhage: cold saline solution intra-drainage flashing Retraction of biliary drainage: co-axial guide-wire removal and repositioning Bilio-pleural Fistula: removal and repositioning of biliary drainage with a lower access (5° or 6° hepatic segment) + pleural drainage |

|